
Where k is the Boltzmann constant (1.38 × 10 −23 J/K), and W is the number of microstates. He developed an equation, known as the Boltzmann equation, which relates entropy to the number of microstates ( W): Ludwig Boltzmann (1844–1906) pioneered the concept that entropy could be calculated by examining the positions and energies of molecules. The Boltzmann Equation Figure 18.2 “Ludwig Boltzmann” Figure 18.1 “Two-Atom, Double-Flask Diagram.” When the stopcock is opened between the flasks, the two atoms can distribute in four possible ways. Thus we can say that it is entropically favoured for the gas to spontaneously expand and distribute between the two flasks, because the resulting increase in the number of possible arrangements is an increase in the randomness/disorder of the system. If we increased the number of atoms, we would see that the probability of finding all of the atoms in the original flask would decrease dramatically following (½) n, where n is the number of atoms. The likelihood of all atoms being found in their original flask, in this case, is only 1 in 4. If we were to take snapshots over time, we would see that these atoms can have four possible arrangements.
#ENTROPY DEFINITION CHEMISTRY FREE#
When the stopcock is opened, both atoms are free to move around randomly in both flasks. At first, both atoms are contained in only the left flask. In this system, we have placed two atoms of gas, one green and one blue. The Molecular Interpretation of EntropyĬonsider the following system, where two flasks are sealed together and connected by a stopcock (see Figure 18.1 “Two-Atom, Double-Flask Diagram”). These definitions can seem a bit vague or unclear when you are first learning thermodynamics, but we will try to clear this up in the following subsections.

But what exactly is entropy? Entropy is typically defined as either the level of randomness (or disorder) of a system or a measure of the energy dispersal of the molecules in the system.
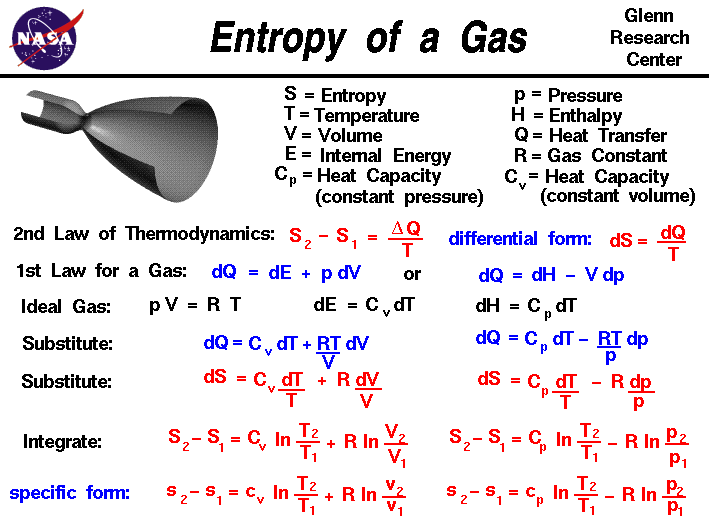
The second law of thermodynamics states that a spontaneous process will increase the entropy of the universe. To assess the spontaneity of a process we must use a thermodynamic quantity known as entropy ( S).

To be able to estimate change in entropy qualitatively.To gain an understanding of the Boltzmann equation and the term microstates.To gain an understanding of the term entropy.It is a measure of how organized or disorganized energy is in a system of atoms or molecules. Thermodynamic entropy is part of the science of heat energy.Information entropy, which is a measure of information communicated by systems that are affected by data noise.The meaning of entropy is different in different fields. These ideas are now used in information theory, statistical mechanics, chemistry and other areas of study.Įntropy is simply a quantitative measure of what the second law of thermodynamics describes: the spreading of energy until it is evenly spread. Some very useful mathematical ideas about probability calculations emerged from the study of entropy. The word entropy came from the study of heat and energy in the period 1850 to 1900. A law of physics says that it takes work to make the entropy of an object or system smaller without work, entropy can never become smaller – you could say that everything slowly goes to disorder (higher entropy).
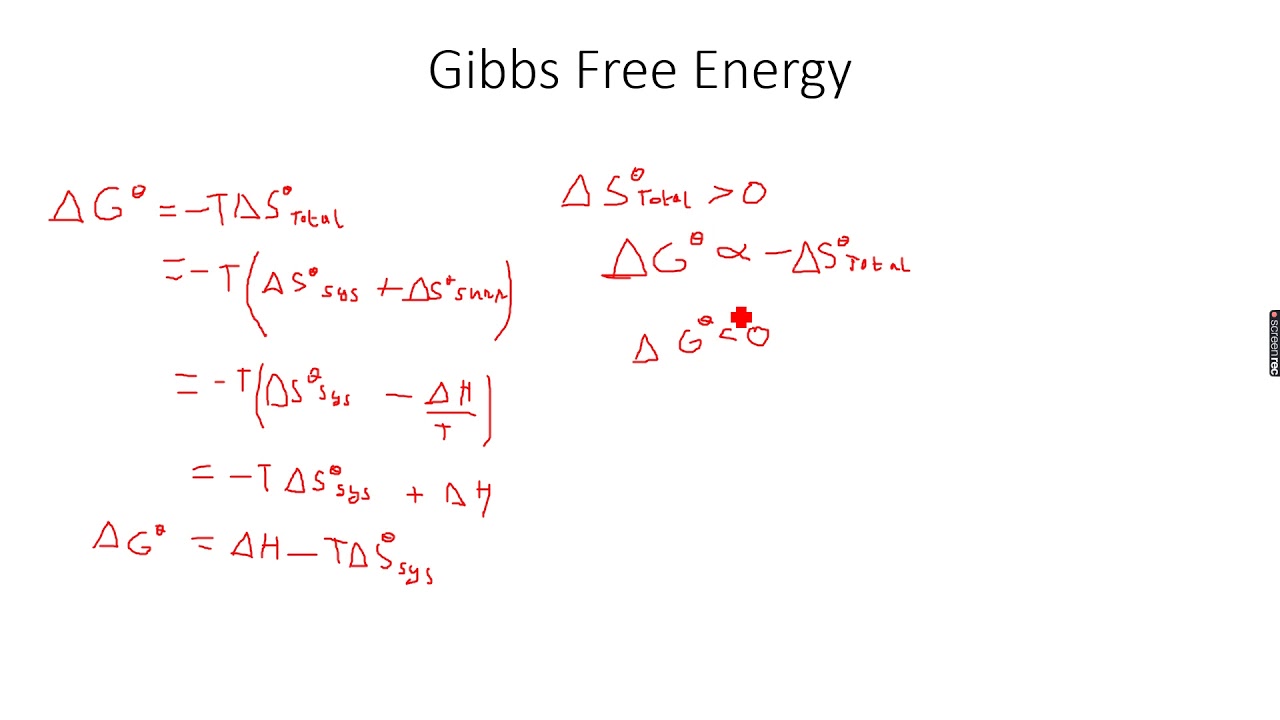
The higher the entropy of an object, the more uncertain we are about the states of the atoms making up that object because there are more states to decide from. In this sense, entropy is a measure of uncertainty or randomness. Entropy is also a measure of the number of possible arrangements the atoms in a system can have. The entropy of an object is a measure of the amount of energy which is unavailable to do work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
